(rev. July 7, 2015)
Notes On Chapter Thirty-Three
-- Trends in Networking Technologies and Uses
- 33.1 Introduction
- Recent developments
- Longer-term research
- 33.2 The Need for Scalable Internet Services
- A centralized server and/or its access network can
become a bottleneck.
- This motivates much investigation and development of scaling
architectures.
- 33.3 Content Caching (Akamai)
- ISPs often cache static web pages.
- Some companies offer a distributed caching service.
- For example, Akamai has a set of servers all over the Internet.
- An organization can pay Akamai for the privilege of pre-loading
Akamai server caches with the organization's web pages.
- Links on the organization's web site direct customer clicks to Akamai
server content.
- The organization is allowed to send updates of their 'content' to the
Akamai caches.
- The scheme reduces load on the servers of the organization.
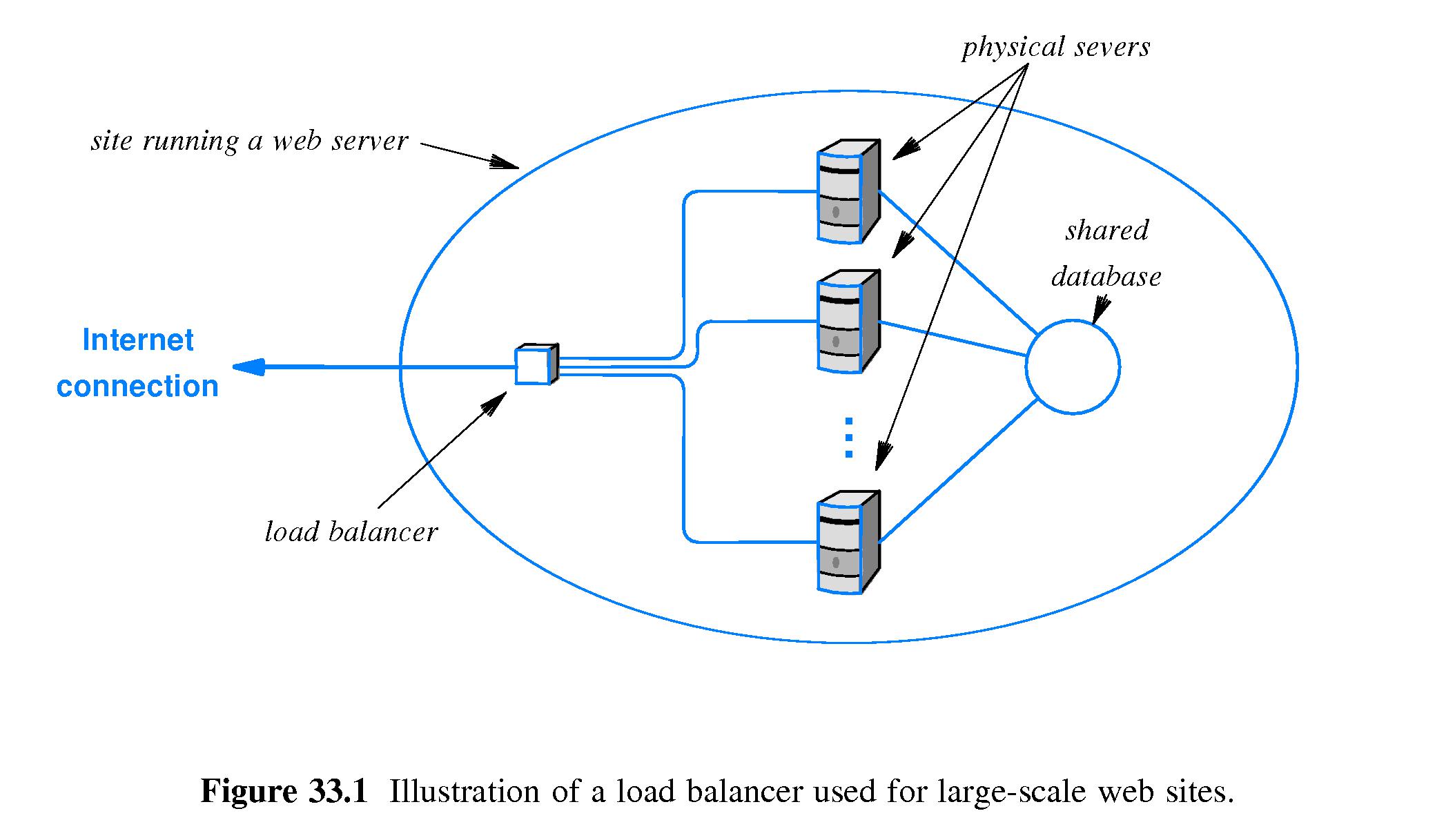
- 33.4 Web Load Balancers
- Refer to Figure 33.1.
- Web server optimization gets a lot of attention because businesses
rely on the web to make sales.
- A load balancer is a device that distributes incoming requests
among multiple computers running identical web servers.
- Typically the servers share the same customer database.
- The load balancers have the ability to direct a series of requests
from the same source to the same server.
- 33.5 Server Virtualization
- Some systems support process migration - the capability of an
executing program to move to another computer.
- Given infrastructure for process migration, it is possible for a
server on an overloaded machine to move to another machine where
resources like CPU time are in more plentiful supply.
- 33.6 Peer-to-Peer Communication
- P2P is a technology used to increase the speed of file downloads.
- Clients fetch pieces of the file.
- Various servers all over the Internet have various pieces of the
file.
- Clients try to fetch pieces from nearby servers.
- Clients agree to be servers for the pieces of the file they have
downloaded.
- Well-known examples were created mainly for downloading music files:
e.g. Napster & Kazaa
- 33.7 Distributed Data Centers and Replication
- Sites such as Google get so much traffic that they have resorted
to another approach.
- When a browser connects with DNS to resolve the name www.google.com,
different IP numbers are 'suggested' at different times.
- This has the effect of balancing the load over multiple Google
data centers distributed in various geographic locations.
- 33.8 Universal Representation (XML)
- XML allows programmers to choose arbitrary tags so the documents
can be understood by multiple applications.
- Documents can include a style sheet that specifies legitimate
document structure.
- Uses:
- on interface between web server and database
- load balancers parsing XML
- XML controlling downloads in mobile devices
- XML representing specifications used by network management
systems
- 33.9 Social Networking
- Starting in the early 2000's there has been a significant increase in
the production of content by individual users - for example blogs,
chats, Facebook, MySpace and YouTube.
- One implication is that the typical user is uploading data more than
previously.
- 33.10 Mobility and Wireless Networking
- Users now expect to be connected continuously to the Internet.
- Wireless technologies receive a lot of attention and are targeted for
rapid development.
- Mobile phone networks are converging with the Internet.
- Mobile computer users rely on WiFi and Virtual Private Networks (VPN)
- 33.11 Digital Video
- Cable companies are replacing analog service with digital.
- Digital TV content is provided over packet networks.
- There is increasing use of IPTV.
- The Internet is converging with the television and radio networks.
- There is less and less difference between computers
and television sets.
- On demand video is easier to deploy this way.
- Pause, rewind, and live-capture are easier to control.
- 33.12 Higher-Speed Access and Switching
- Some cellular providers data rates up to 50 Mps.
- Some ISPs offer Gigabit speeds to residential customers.
- Backbone network links may soon reach rates of 40 Gbps.
- It's not far-fetched to predict such rates will be provided to homes
and small businesses in the not-to-distant future.
- That is enough bandwidth for high-definition video.
- 33.13 Cloud Computing
- Companies outsource IT operations to cloud providers
that maintain data centers that include computational and storage
services.
- Flexibility is a big advantage. Companies only pay for what they
use and they don't have to provision their local shops
for peak resource consumption.
- 33.14 Overlay Networks
- Computers connected to the Internet can utilize tunneling.
- When X transmits a packet to Y, X encapsulates the packet in
an outer datagram.
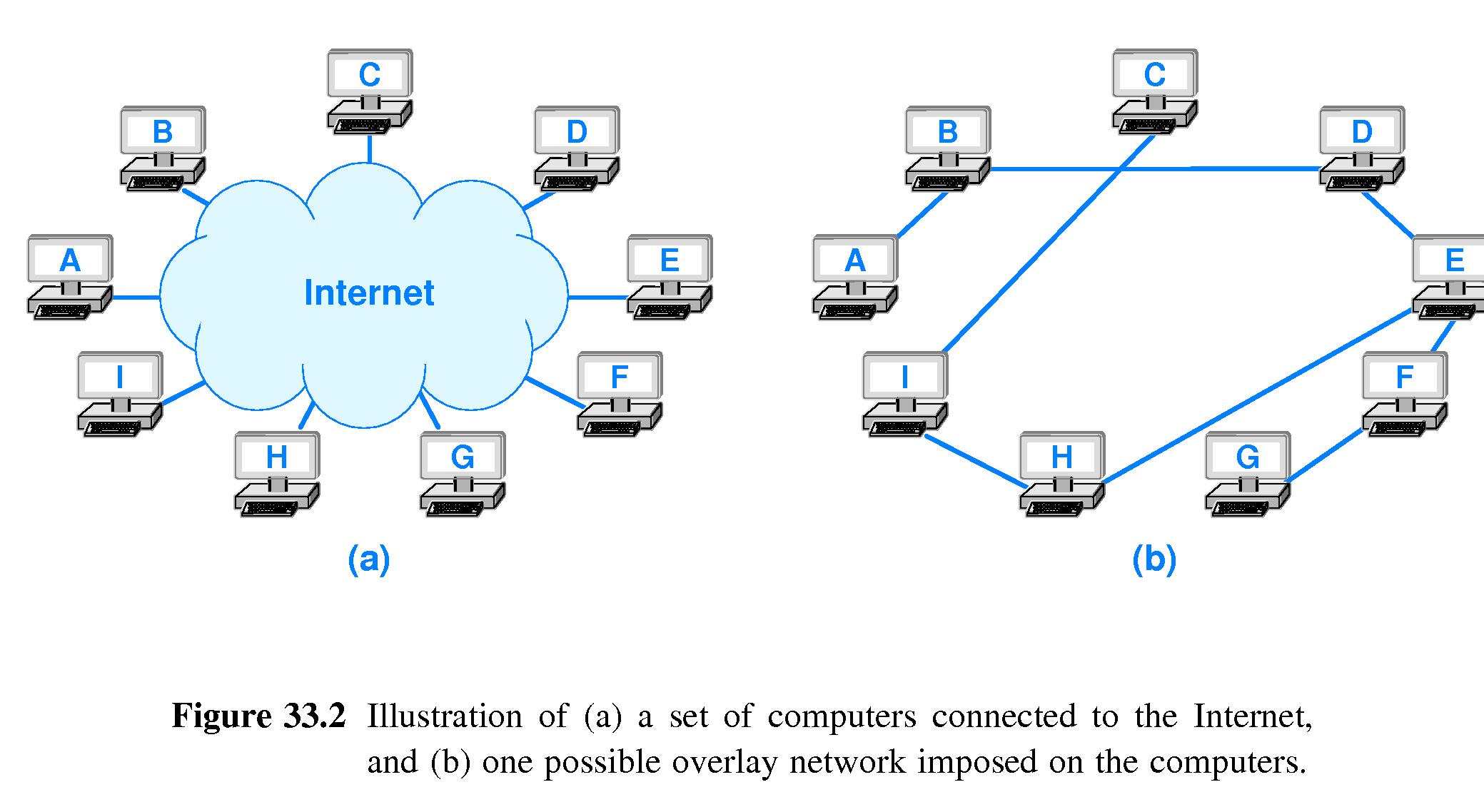
- The intermediate computers on the route don't need to use the the
contents of the inner datagram, which is encrypted by the sender.
- This scheme can also be used to partition the network logically,
so that certain traffic is restricted to only certain machines.
- Any points of intersection of separate networks can be chosen with
care and hardened.
- Switches and/or routers can also define tunnels.
- 33.15 Middleware
- Middleware facilitates coordination among applications running on multiple
platforms.
- Middleware typically operates at the level between applications
and the operating system.
- Shibboleth is an example, which provides password management and validation
across a set of organizations.
- 33.16 Widespread Deployment of IPv6
- IPv4 has adapted much better than many people expected.
- We are somehow doing without much penetration of IPv6.
- We could remove NAT from the Internet and have end-to-end addressing
everywhere but it would require replacing a huge amount of networking
equipment and software.
- There's no actual need for IPv6 now, but the transition has started,
and it will continue.
- Google wants IPv6 so that all devices will have unique addresses -
that way Google can target ads more individually.
- Cellular operators know they have to replace equipment when they transition
to IP, and they don't want to gamble on using IPv4.

