(rev. 2015/02/08)
Notes On Chapter Five
-- Overview of Data Communications
- 5.1 Introduction
- Transmission of information across media
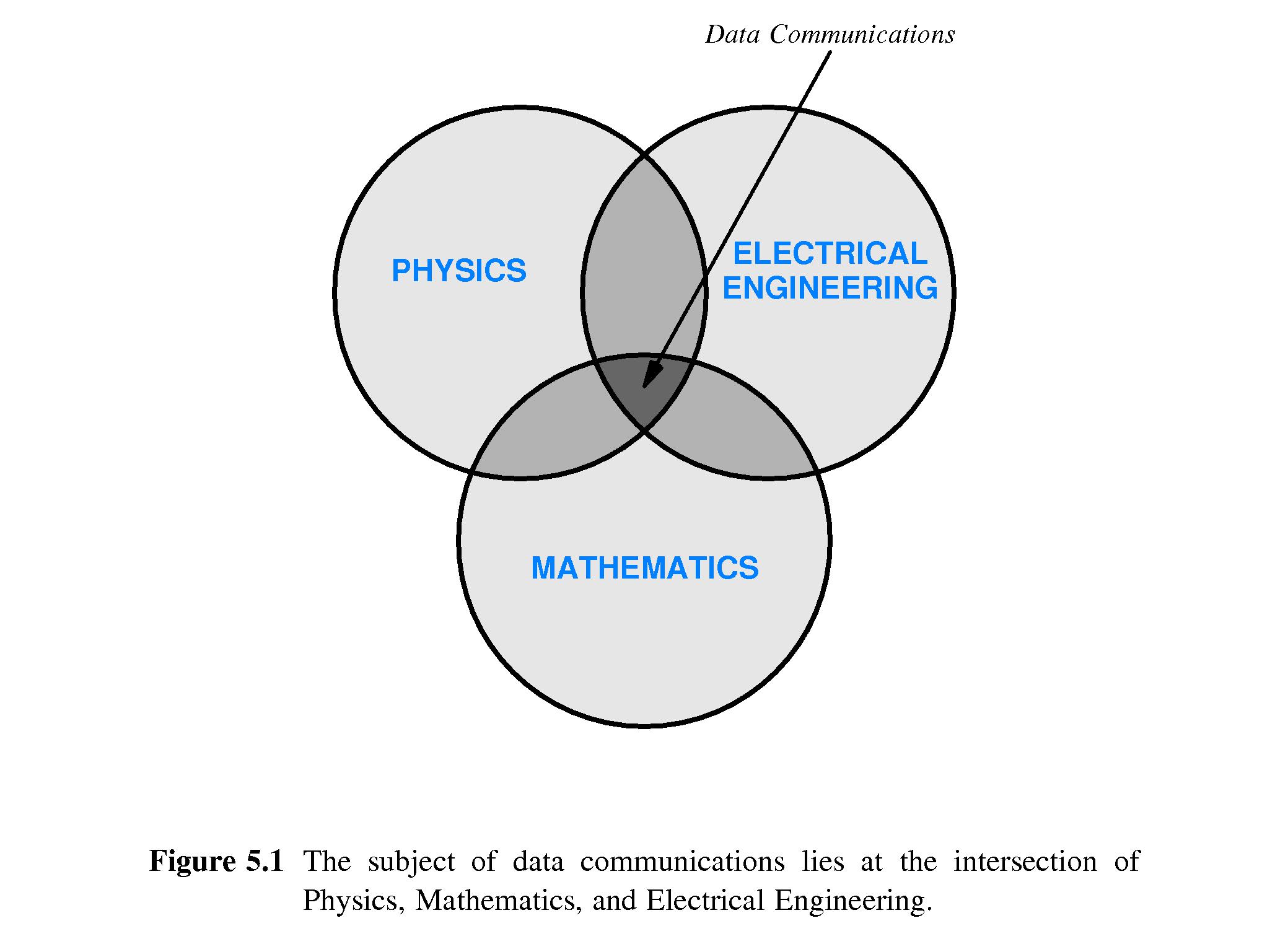
- 5.2 The Essence of Data Communication
- The subject involves concepts from mathematics, physics and
electrical engineering.
- 5.3 Motivation and Scope of the Subject
- sources of info can be of arbitrary types
- transmission uses a physical system
- multiple sources of information may be able to share a medium
- real physical systems have limitations
- 5.4 The Conceptual Pieces of a Communication System
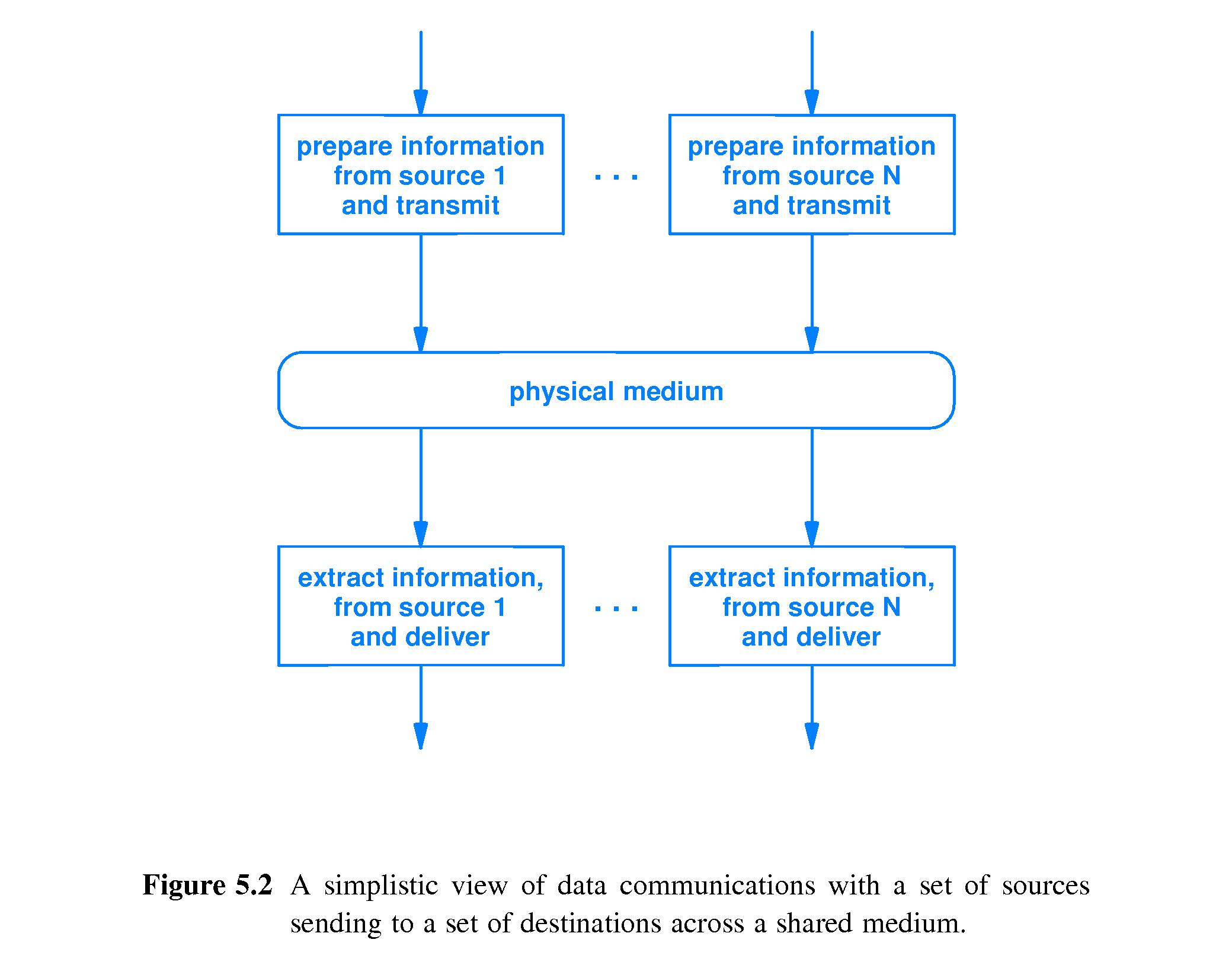
- Transmitting multiple sources of information across a shared medium
is not as simple as it may seem. It doesn't "just work" if a bunch
of people shout at each other in a hallway.
- Issues:
- encoding information (e.g. digitizing)
- encrypting information
- error detection and correction
- multiplexing/demultiplexing
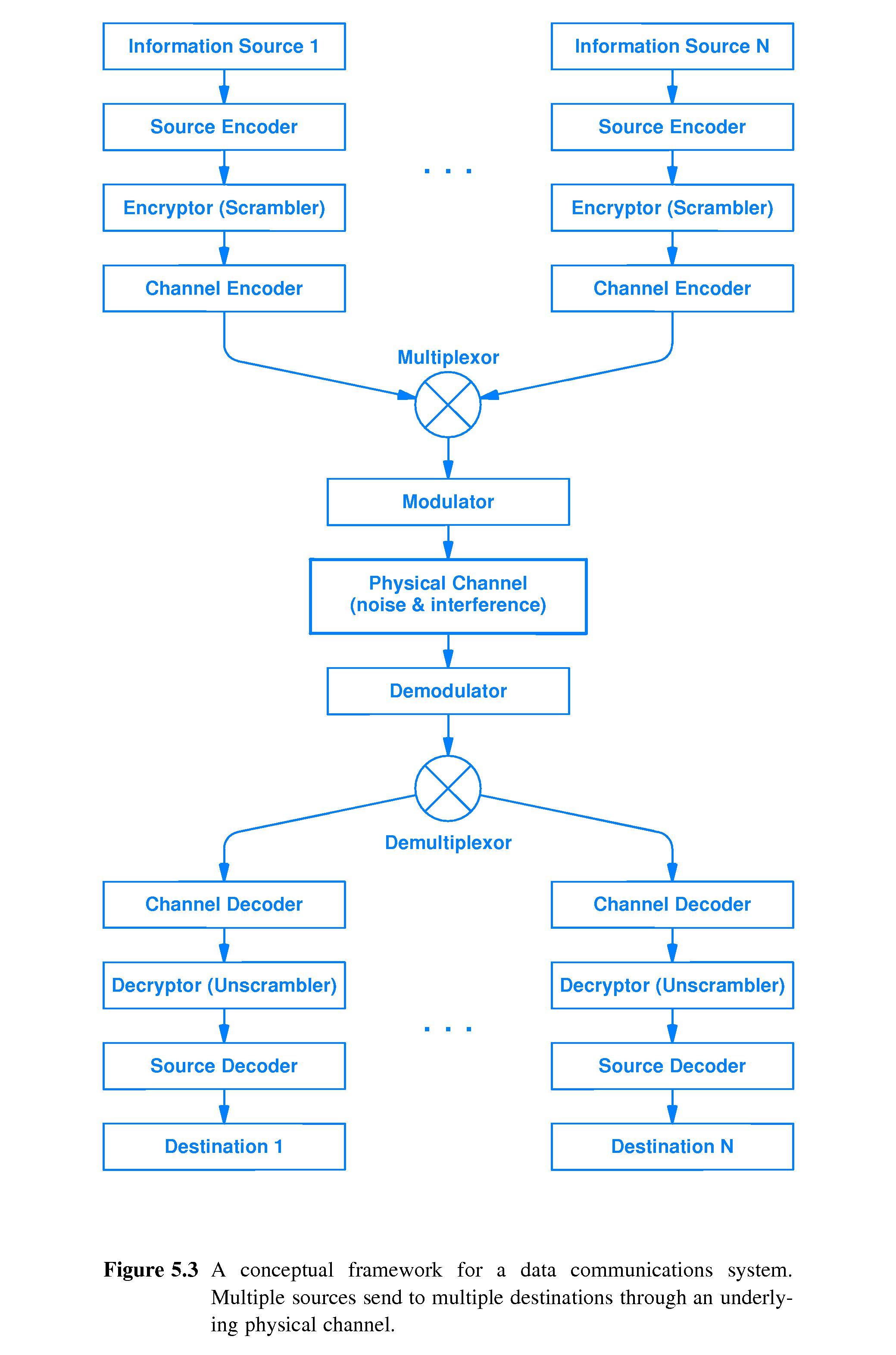
- 5.5 The Subtopics of Data Communications
- Sources of information can be analog or digital.
- There are reasons to transform one digital form into another, for
example to achieve compression.
- Security considerations may require the addition of encryption.
- Channel coding for detection and correction of errors in bit values
- Mulitplexing/Demultiplexing - ways to combine different streams of
information for transmission and separate them out at the
destination.
- Modulation/Demodulation - e.g digitizing for transmission and then
translating back into analog at the destination.
- Properties of Physical Channels - e.g. bandwidth, noise, interference,
channel capacity, and transmission modes: serial and parallel.


