- change to networking and Internet
- Internet motivation: centralized to distributed
- Internet applications
- communication paradigms
- programming interface
- The purpose of early forms of computer networks was to connect multiple users to a single large computer.
- People soon also wanted networks to allow sharing of peripherals such as printers and disk-based file systems.
- At the time that the Internet got its start, the sharing of powerful computers was important to researchers working at government laboratories. Computers were expensive and sharing was seen as a way to save money.
- The Department of Defense is also said to have been interested in developing a network that could continue to function even after being heavily damaged.
- ARPA put together a large group of the best and brightest individuals available. They created the ARPANET, and later the Internet.
- ARPANET was developed all through the 1970's and 1980's. Gradually, it became better known as the Internet. The military part, MILNET, was split off and the non-military part of the Internet was run by The National Science Foundation (NSF) for a while. At first it was devoted mainly to education and research. It became increasingly commercialized in the 1990's.
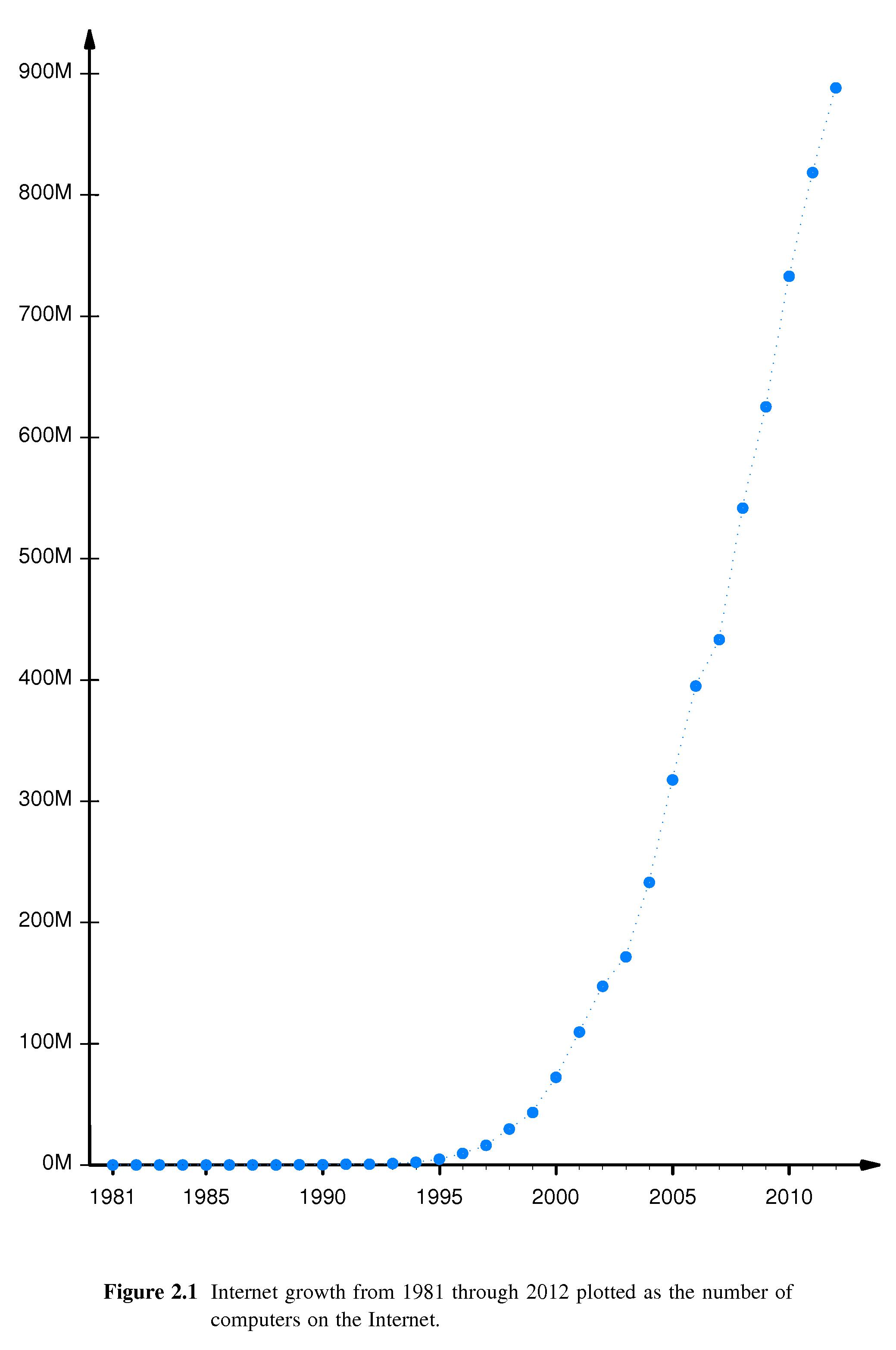
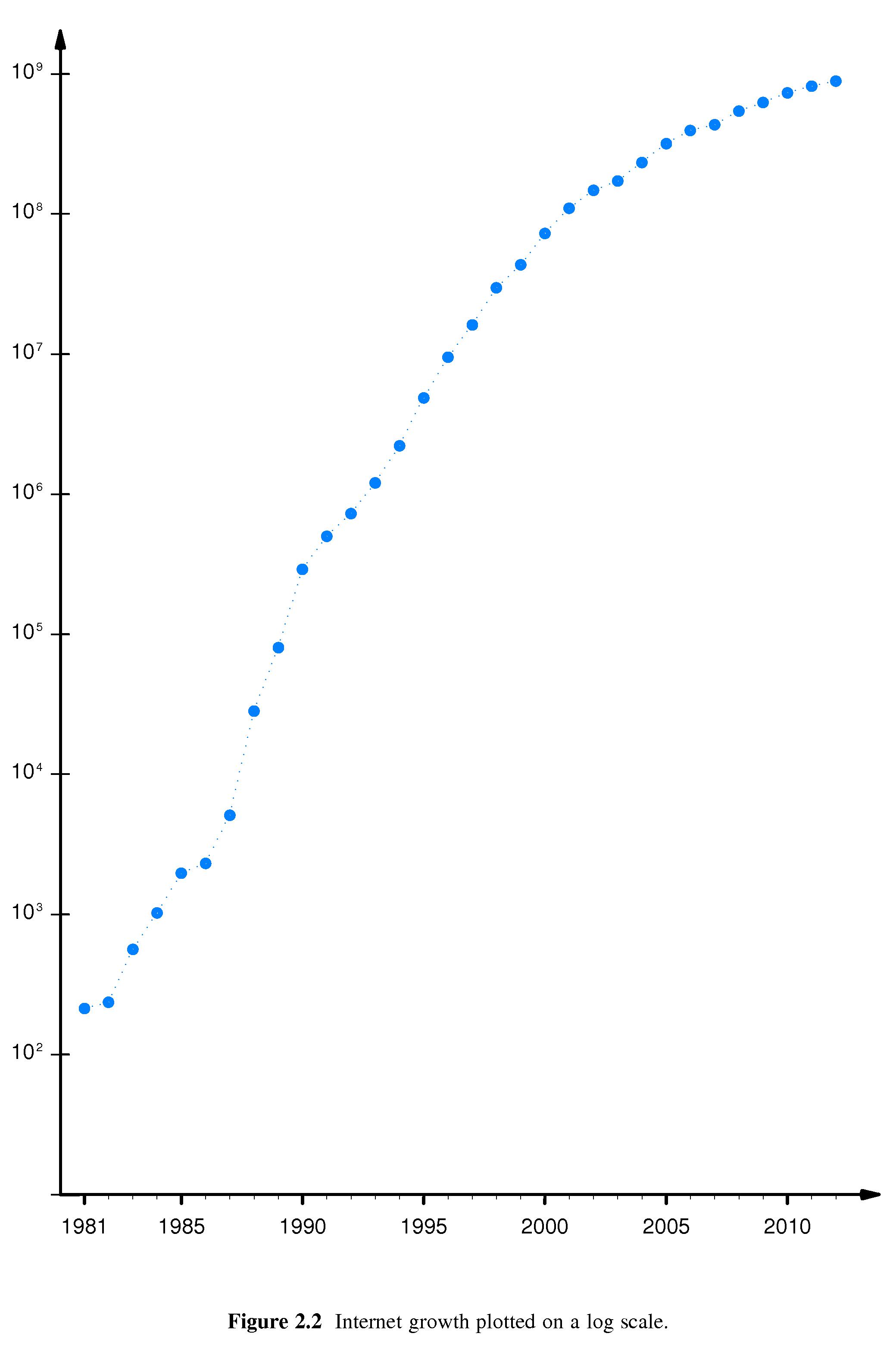
- Plots show that the number of hosts (computers) on the Internet approximately doubled every 9-14 months from 1981 through the present.
- What has been the relative growth in various areas of the world?
- Now that computing equipment is cheap and powerful, the original emphasis on resource sharing has shifted.
- The sharing of information (communication) on the Internet is now much more important that the sharing of hardware.
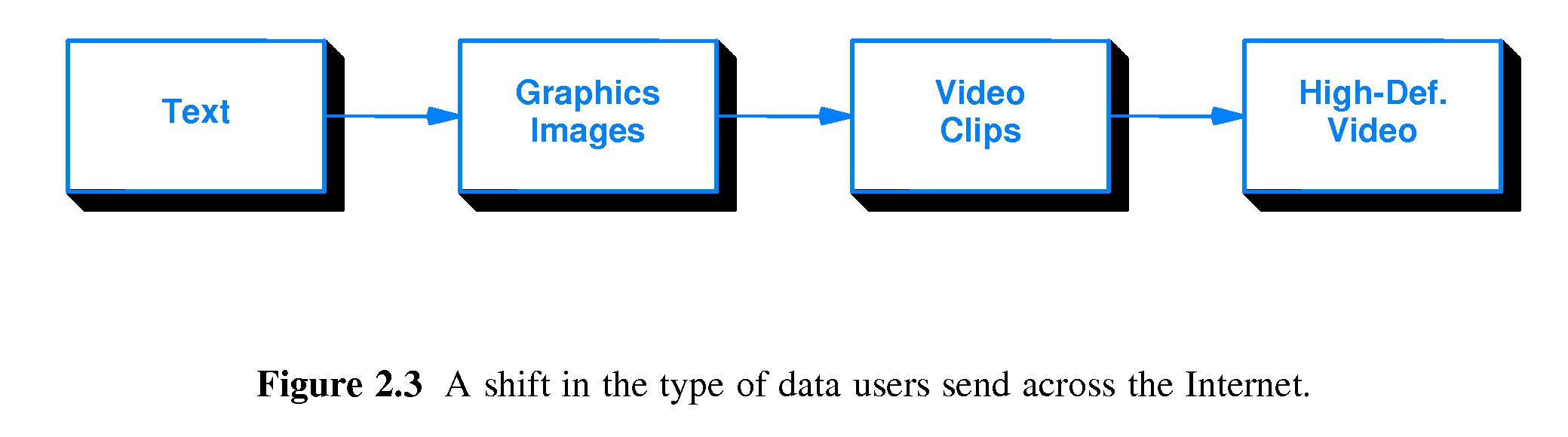
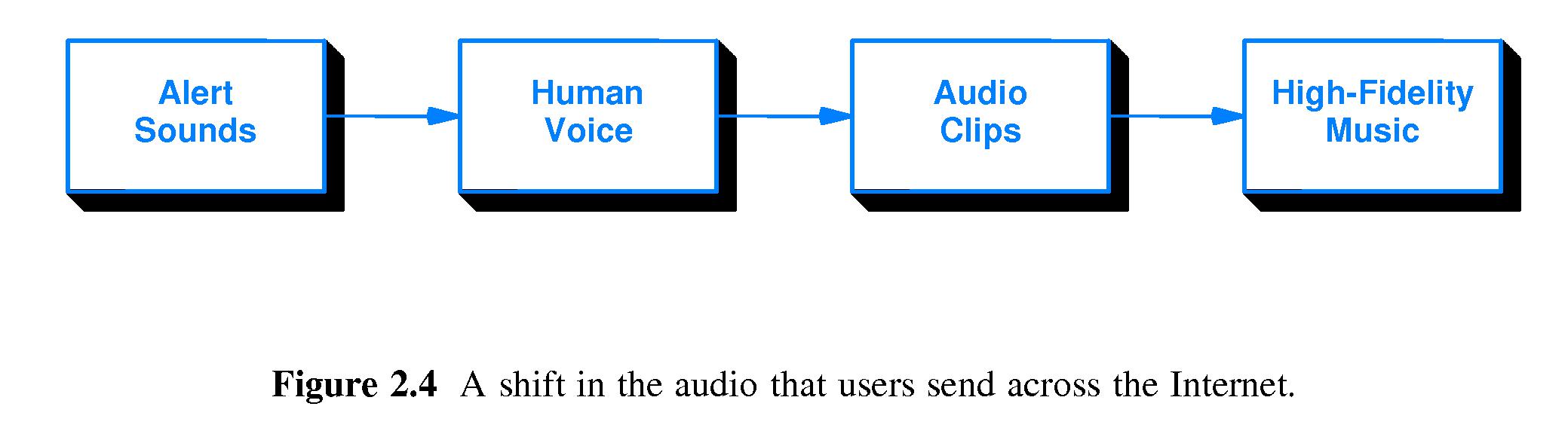
- Early on, most of the data on the Internet was text. Today much of it is high-fidelity audio and high-resolution video.
- There has been a similar progression of audio content.
- Telephone: Voice over IP (VoIP)
- Cable Television: Switch to digital and IP delivery
- Cellular: Switch from analog to digital (3G)
- Internet Access: Switch from wired to wireless (Wi-Fi)
- Data Access: Switch from centralized to distributed (P2P)
- Social Networking: Consumers, volunteer organizations
- Sensor Networks: Environment, security, fleet tracking
- High-Quality Teleconferencing: Business-to-business communication
- Online banking and payments: Individuals, corporations, governments
Social networking facilitates people's efforts to find others with shared interests.
- With the advent of cloud computing, we see increased emphasis on forms of sharing that were important when computer networks began: the use of simple devices to access centralized computing and storage resources.
- Location Independence: Portable wireless access devices allow users to change their locations, yet effortlessly maintain access to resources.
- The cloud provider backs up user data, and takes care of the maintenance of the cloud hardware and the software, which means less work for clients.
- Companies can be clients of cloud service providers, and these companies can benefit from the elasticity of cloud service - not required to pay continuously for service they only need from time to time.