(rev. 01/26/2008)
Notes On Chapter Thirty-Eight
-- RPC and Middleware
- 38.1 Introduction
- Tools for making client-server software
- 38.2 Programming Clients and Servers
- If one programs with the socket Application
Programming Interface (API), it's easy to make errors
that are hard to detect, but which can cause big problems.
- There are (middleware) tools that can
eliminate some of those errors - by generating code automatically
... programs that write programs.
-
 38.3 Remote Procedure Call Paradigm
38.3 Remote Procedure Call Paradigm
- In the Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
approach, the programmer works with a
conventional API, and special
middleware software generates the code to handle the network
communication details.
- The effect is that the client software appears to make procedure
calls that execute on the server.
-
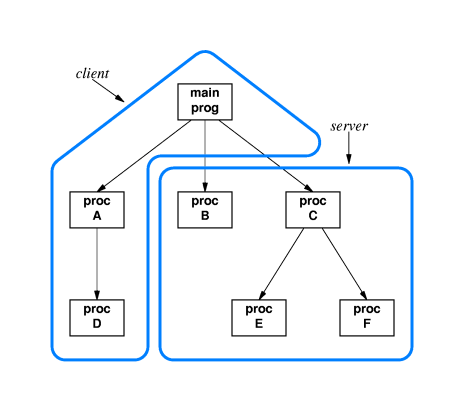 38.4 RPC Paradigm:
38.4 RPC Paradigm:
- The programmer
- designs a conventional program,
- uses an Interface Definition Language (IDL) to partition the call graph of the program
into client and server parts, and
- uses an RPC tool (middleware) to create software that
handles the network communication.
- 38.5 Communication Stubs
-
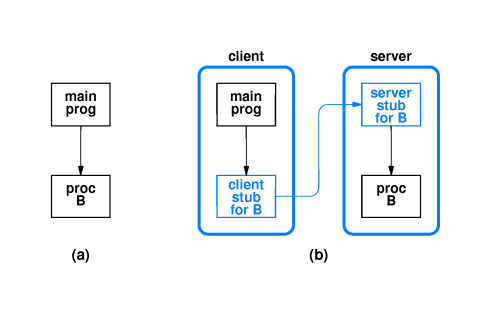 When a call is made to a non-local procedure:
When a call is made to a non-local procedure:
- A stub on the client
- intercepts the procedure call,
- gathers (marshals) values for arguments,
- sends a message across the network to a stub on the
server,
- receives results, and
- returns results to the caller exactly like a local
procedure call would.
- The stub on the server
- receives the message from the client stub,
- invokes the desired procedure, and
- sends the results back to the client stub.
- 38.6 External Data Representation
- Data Conversion Problem: When a client
invokes a remote procedure, parameters must be passed from client to
server. The two hosts may have different ways of representing data
(e.g. big-endian versus little-endian.)
- A popular way to deal with this:
- client converts the data to a standard external data
representation (XDR),
- client transmits to server, and
- server converts from the XDR to its local representation.
- 38.7 Middleware And Object-Oriented Middleware
- These days programmers frequently use object-oriented programming
languages. Consequently we now have middleware
that supports distributed objects and remote method
invocation as well as remote procedure call.
- 38.7.1 ONC RPC
- Open Network Computing Remote Procedure Call (ONC RPC,
aka Sun RPC)
- 38.7.2 DCE/RPC
- Open Software Foundation's Distributed Computing
Environment (DCE)
- 38.7.3 MSRPC
- Microsoft Remote Procedure Call (MSRPC)
- 38.7.4 CORBA
- Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA)
- CORBA has the ability to create proxies (similar to stubs) at
runtime.
- 38.7.5 MSRPC2
- Microsoft Remote Procedure Call, Second Generation
(MSRPC2, aka Object RPC, aka ORPC)
- 38.7.6 COM/DCOM
- Component Object Model (COM) and Distributed
Component Object Model (DCOM)
- 38.7.7 Java RMI
- Java Remote Method Invocation (Java RMI)
- 38.7.8 Jini
- "Jini" is not an acronym.
- Jini supports process migration.
- 38.7.9 SOAP
- Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP)
- 38.7.10 UDDI
- Universal Discovery Description and Integration (UDDI)
- UDDI is a registry mechanism, not an RPC mechanism.
- UDDI can be used with RPC mechanisms.
- 38.7.11 XML
- Extensible Markup Language (XML)
- Many applications that use RPC also use an XML encoding.
- 38.8 Summary
 38.3 Remote Procedure Call Paradigm
38.3 Remote Procedure Call Paradigm  38.4 RPC Paradigm:
38.4 RPC Paradigm:  When a call is made to a non-local procedure:
When a call is made to a non-local procedure: